Review
Everything You Need to Know About Furnace Flame Sensors
AZparts Team
Updated on November 28, 2025
10 min read
Maintaining your home's heating system is crucial for both comfort and safety, especially during colder months. Among the many components that ensure your furnace operates efficiently and safely, the flame sensor plays a vital role that's often overlooked until problems arise. In this comprehensive guide, AZParts explore what a furnace flame sensor is, how it works, and why it's essential for your home's safety.
1. What is a Furnace Flame Sensor?
A furnace flame sensor is a small part of furnace but critical safety device installed in gas-powered furnaces and heating systems. Typically appearing as a thin metal rod, this component is positioned directly in the path of the burner flame. Its primary function is to detect whether the furnace's gas burners have successfully ignited when the heating cycle begins.
The sensor consists of a metal rod (usually made of stainless steel) often with a porcelain base that provides insulation. Though small in size, generally just a few inches long, this device plays an outsized role in your furnace's operation and your home's safety.

What is a furnace flame sensor (Source: AZParts)
2. The Importance of a Furnace Flame Sensor
The flame sensor serves as a crucial safety mechanism that prevents potentially dangerous situations in your home heating system. Without this vital component, your furnace could release unburned gas into your home if the burners fail to ignite properly, creating serious risks:
- Prevents gas leaks: If your furnace attempts to ignite but fails, the flame sensor ensures the gas valve closes, preventing unburned gas from accumulating.
- Reduces carbon monoxide risks: By confirming proper combustion, the flame sensor helps prevent the production and release of carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and potentially lethal gas.
- Protects against fire hazards: By ensuring gas is only flowing when a flame is present, the sensor significantly reduces the risk of fire or explosion from gas buildup.
- Prevents furnace damage: The sensor protects the furnace itself from damage that could occur if gas were to flow without proper combustion.
In essence, this small component acts as a vigilant guardian, continuously monitoring your furnace's operation to keep your home and family safe. The importance of this safety feature cannot be overstated, as it's often the last line of defense against potentially catastrophic gas-related accidents.
3. What Does a Furnace Flame Sensor Do?
The flame sensor works through a process that relies on the unique electrical properties of flames. Here's how it functions:
3.1. The Detection Process
- Startup sequence: When your furnace begins a heating cycle, the control board initiates the ignition sequence, opening the gas valve to supply fuel to the burners.
- Flame rectification: Once the burners ignite, the flame makes contact with the metal rod of the sensor. Flames have a unique property called "flame rectification" which allows them to conduct electricity in only one direction.
- Electrical signal generation: The flame sensor harnesses this property by sending a small alternating current (AC) through the rod. When the flame touches the rod, it converts some of this AC current into direct current (DC), creating a small but measurable electrical signal in the microamp range.
- Verification: The furnace's control board monitors this electrical signal. The presence of this small DC current confirms that a flame exists and that gas is being burned properly.
- Safety response: If the control board doesn't detect this signal within a few seconds of the gas valve opening (typically 3-7 seconds), it assumes no flame is present. As a safety measure, it immediately shuts off the gas supply to prevent unburned gas from accumulating.
3.2. The Cycle Continues
During normal operation, this process happens automatically at the start of each heating cycle. The flame sensor continuously monitors for proper combustion throughout the cycle, standing ready to trigger a shutdown if the flame disappears unexpectedly.
It's worth noting that this system is designed to fail safely. If anything prevents the sensor from detecting the flame, whether due to a dirty sensor, a faulty component, or an actual absence of flame, the result is the same: the gas valve closes, and the furnace shuts down.

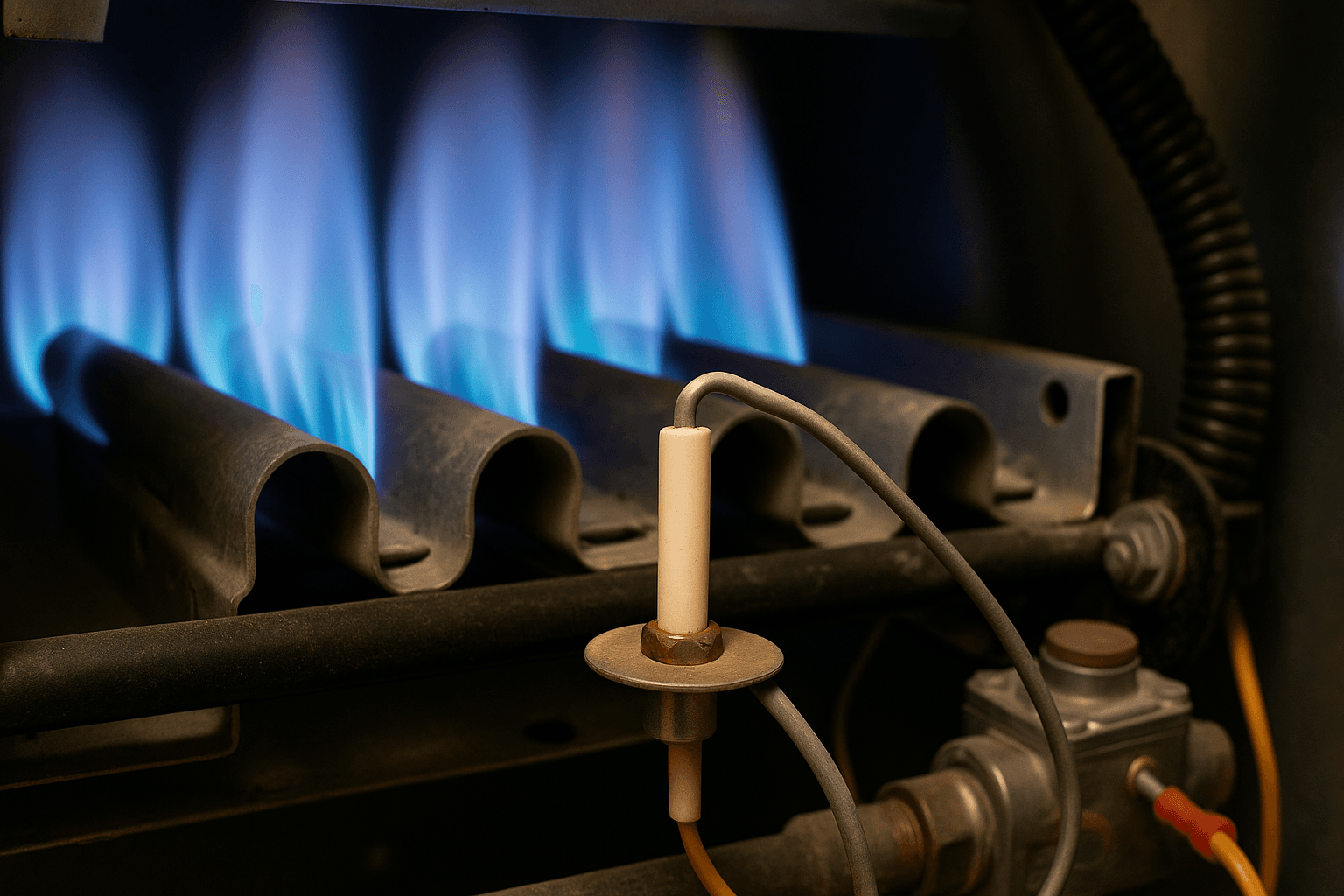
What does a furnace flame sensor do? (Source: Pinterest)
4. Types of Furnace Flame Sensors
While all flame sensors serve the same fundamental purpose, there are several different types used in modern heating systems, each with its own advantages and applications.
4.1. Flame Rectification Sensor (Flame Rods)
The flame rectification sensor, commonly known as a flame rod, is the most prevalent type found in residential gas furnaces. This sensor utilizes the flame's ability to conduct electricity in only one direction (rectification).
How it works: A small AC current is applied to the metallic rod. When the flame touches the rod, it acts as a rectifier, converting some of the AC current to DC. The control system detects this DC component, confirming the presence of a flame.
Advantages:
- Simple and reliable design
- Cost-effective
- Easy to clean flame sensor and maintain
- Works well in most residential applications
If you're looking for reliable flame sensors for your heating system, AZParts offers a range of high-quality options.

Flame rod is the most prevalent type found in residential gas furnaces (Source: AZParts)
4.2. Ultraviolet (UV) Flame Detectors
UV flame detectors operate on a different principle, detecting the ultraviolet radiation emitted by flames rather than using electrical conductivity.
How it works: These sensors contain a UV-sensitive tube or semiconductor that responds to the ultraviolet light emitted during combustion. When UV radiation from a flame is detected, the sensor signals the control system that combustion is occurring.
Advantages:
- Extremely fast response time (nearly instantaneous)
- Can detect flames from various fuels
- Works at greater distances from the flame
- Not affected by contamination the same way flame rods are
Limitations:
- More susceptible to false alarms from other UV sources (like arc welding or lightning)
- Typically more expensive than flame rectification sensors
- Generally found in larger commercial or industrial applications rather than residential furnaces

Ultraviolet (UV) flame detectors (Source: Pinterest)
4.3. Infrared (IR) Flame Detectors
Infrared flame detectors sense the infrared radiation produced by the hot gases of combustion.
How it works: These sensors contain elements sensitive to infrared wavelengths. Advanced models can distinguish between the specific IR signature of flames and other heat sources based on the wavelength and flicker patterns.
Advantages:
- Can function effectively in smoky or dusty environments
- Less susceptible to certain types of interference
- Can detect flames from a greater distance
- Some models can discriminate between different types of fires or fuels
Limitations:
- Can be triggered by other hot objects
- More complex and expensive than flame rods
- More commonly used in industrial settings rather than residential furnaces

Infrared (IR) flame detectors (Source: Pinterest)
4.4. Others
Several other flame detection technologies exist, though they're less common in residential furnaces:
Visible Light (Video) Flame Detectors:
- Use video analytics to analyze visible light patterns associated with flames
- Can differentiate between actual flames and false triggers
- Primarily used in specialized industrial applications
Thermal (Heat) Detectors:
- Detect rapid temperature increases indicative of combustion
- Slower response time than other sensors
- Used in environments where other detector types might produce false alarms
Ionization Flame Detectors:
- Work on principles similar to flame rectification
- Used in specific industrial applications
- Not commonly found in home furnaces
Acoustic Flame Detectors:
- Identify unique ultrasonic acoustic signatures produced by flames
- Primarily used in high-pressure industrial environments
- Rare in residential applications
Most residential gas furnaces rely on the simple and effective flame rectification sensor (flame rod) technology, though understanding the alternatives helps provide context for how these critical safety devices have evolved.
5. Warning Signs of a Malfunctioning Flame Sensor
Recognizing the signs of a failing flame sensor can help you address issues before they lead to complete system failure or safety concerns. Here are the key indicators that your furnace flame sensor may need attention:
- Short Cycling: Furnace starts but shuts down within 30 seconds to a few minutes because the dirty or faulty sensor fails to detect the flame.
- Yellow or Orange Flames: Healthy gas flames should be primarily blue; yellow or orange flames indicate incomplete combustion possibly related to flame sensor issues.
- Visible Damage: Look for cracks in the porcelain insulation, corrosion on the metal rod, carbon buildup on the sensor tip, or misaligned positioning.
- Increased Utility Bills: Intermittently working sensors cause inefficient furnace operation, leading to higher gas consumption despite seemingly normal operation.
- Unusual Odors: Incomplete combustion due to flame sensor issues may produce strange smells around your furnace or coming from vents.
- Constant Thermostat Adjustments: If you're frequently adjusting your thermostat because your home isn't reaching set temperatures, the sensor may be preventing complete heating cycles.
- Error Codes: Modern furnaces display diagnostic codes through blinking LEDs on the control board that often indicate flame sensor problems.
- Cold Air From Vents: When the blower runs but only cold air comes out, this may indicate the flame sensor is preventing burners from staying lit.
Addressing these warning signs promptly can prevent more serious furnace problems and ensure your heating system operates safely and efficiently.

Warning signs of a malfunctioning flame sensor (Source: Freepik)
6. FAQs about furnace flame sensor
6.1. What is the Lifespan of a Furnace Flame Sensor?
A typical furnace flame sensor lasts 10-20 years before replacement becomes necessary. Factors affecting its longevity include usage patterns, air quality, installation quality, and regular maintenance. Homes in colder climates with longer heating seasons or environments with poor air filtration may experience faster sensor degradation, requiring more frequent inspection and maintenance.
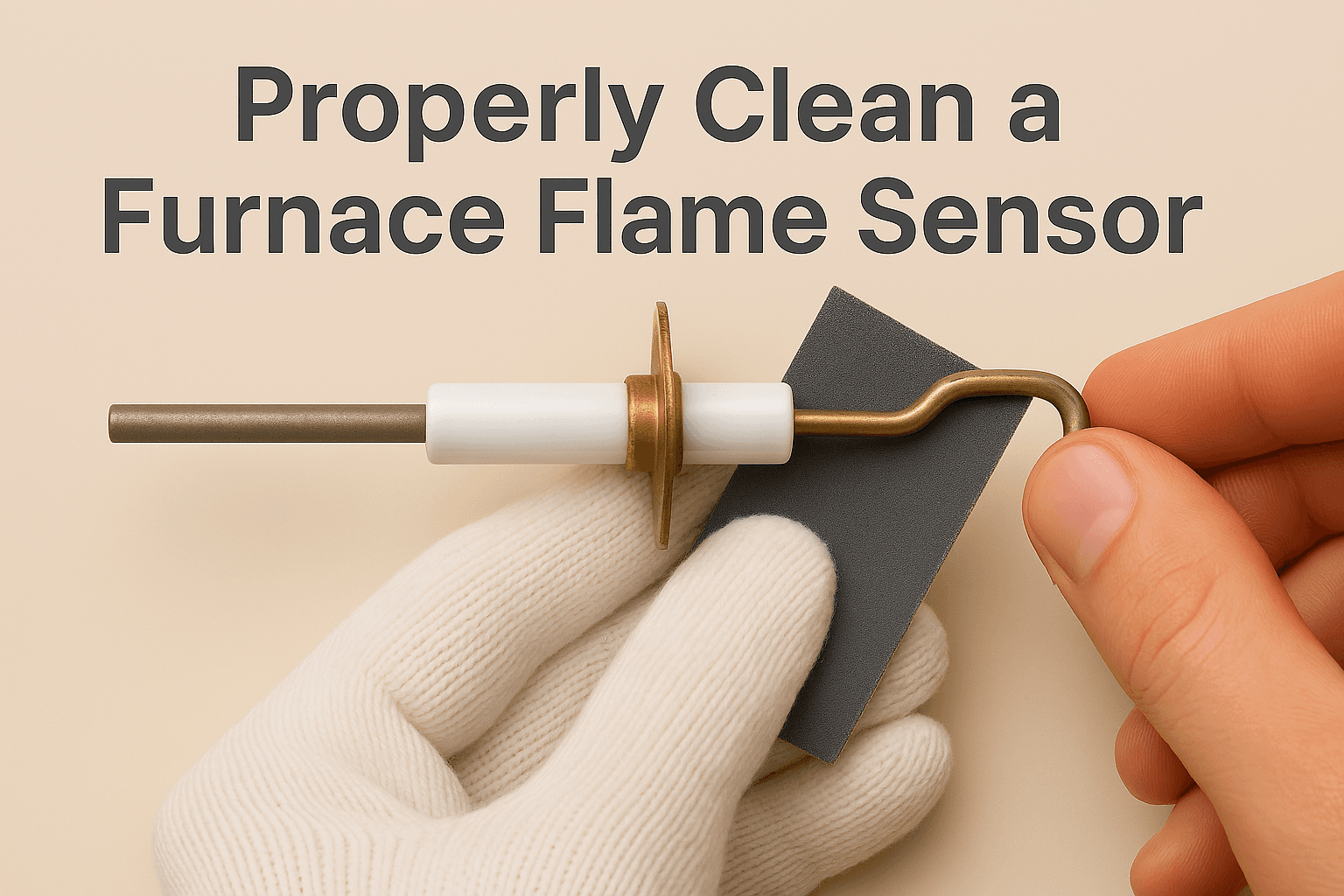
6.2. How to Clean and Maintain Your Furnace Flame Sensor
To clean your furnace flame sensor, turn off power and gas, remove the front panel, and locate the sensor near the burner assembly. Gently clean only the metal rod portion with fine-grit sandpaper or a dollar bill, avoiding the ceramic base. After reinstalling the sensor in its original position, restore power and gas, and remember to perform this maintenance annually before the heating season.
6.3. What happens when a furnace flame sensor goes bad?
When a furnace flame sensor fails, safety mechanisms trigger short-cycling—the furnace starts but quickly shuts down before completing a heating cycle. Signs include delayed ignition, cold air from vents, or the furnace entering "lockout" mode after several failed attempts. The control board interprets the absence of flame detection as hazardous and halts gas flow to prevent dangerous gas buildup.
6.4. Will a furnace run without a flame sensor?
No, a modern furnace cannot operate safely without a working flame sensor, as this essential safety component prevents hazardous gas buildup. Bypassing or running without this device creates severe safety risks including potential gas leaks, carbon monoxide poisoning, and fire hazards. The furnace control board specifically requires the electrical signal from the flame sensor to maintain gas flow and complete normal heating cycles.
6.5. What is the difference between a flame sensor and a temperature sensor?
A flame sensor detects flame presence through electrical conductivity (flame rectification), while temperature sensors merely measure heat levels without verifying combustion. Flame sensors function as primary safety components that prevent gas flow without ignition, whereas temperature sensors monitor system performance and comfort settings. Though both may exist in a furnace system, they have distinct purposes, flame sensors ensure safety and proper ignition, while temperature sensors regulate heating cycles.
Your furnace's flame sensor, despite its small size, is critical for home heating safety and efficiency. Understanding this component's function, recognizing failure symptoms, and implementing regular maintenance prevents system breakdowns while maximizing furnace lifespan. DIY cleaning is possible for confident homeowners, but professional HVAC technicians offer expert service when needed.
Remember that while cleaning can resolve many flame sensor issues, replacement is sometimes necessary. If you need a replacement flame sensor or other furnace parts, AZParts offers a wide selection of high-quality components for virtually all major furnace brands and models.
Contact Info
Address: 8 The Green, Ste A, Dover, Delaware 19901-3618, United States
Email: support@azparts.com
Furnace
Further Reading
Further Reading