Review
What Are the Parts of a Lawn Mower?
AZparts Team
Updated on November 19, 2025
12 min read
Understanding the names and functions of lawn mower parts is essential for proper maintenance and timely repairs. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or just want to communicate better with repair technicians, knowing parts like blades, spark plugs, filters, and handles can make all the difference. In this guide, AZParts helps you identify key mower components to keep your lawn looking its best year-round.
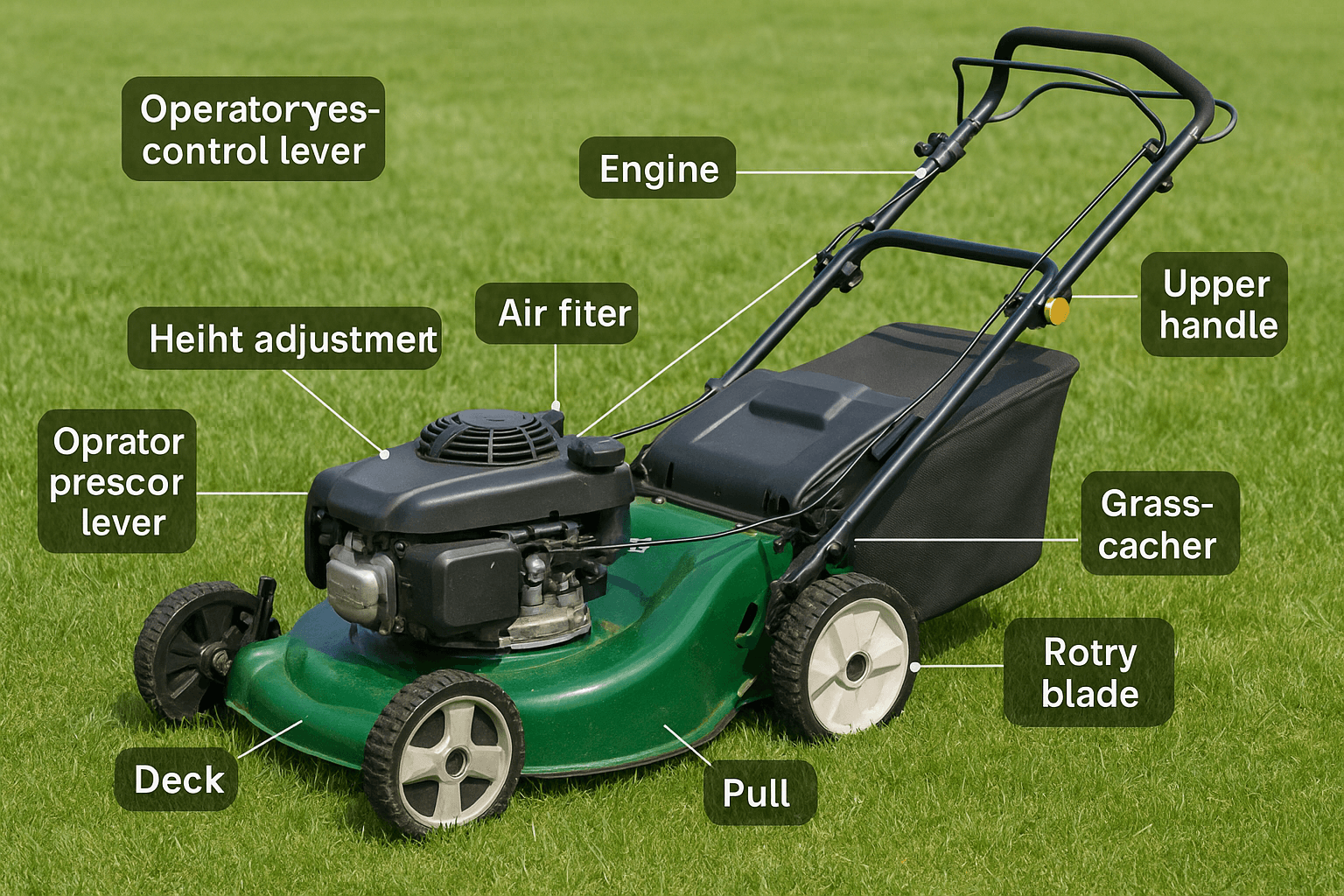
1. Main Engine Components of Lawn Mowers

Main Engine Components of Lawn Mowers Location (Source: AZParts)
1.1. Fuel Tank / Fuel Valve
Location: Usually located on the side or top of the mower's engine, the fuel tank is often made of plastic or metal and has a cap for refueling.
Function: The fuel tank stores gasoline, which is essential for powering the lawn mower’s engine. It supplies fuel through the carburetor to keep the engine running smoothly.
How to Fix When Malfunctioning: If your mower is hard to start or stalls during use, the fuel tank could be the source of the problem.
- Empty the tank if the fuel is stale or has debris.
- Fill it with new, high-quality gasoline.
- Use a fuel stabilizer to extend the fuel's shelf life and improve performance.
- Inspect the gas cap vent and clean or replace it to allow proper airflow and avoid pressure issues.
1.2. Carburetor
Location: Mounted on the side of the engine, typically between the air filter and the engine block.
Function: Mixes air and fuel in the proper ratio to create a combustible mixture that powers the engine. This mixture is then delivered to the combustion chamber where it ignites and drives the piston.
How to Fix When Faulty: If the engine starts momentarily with starter fluid but stalls shortly after, the carburetor is likely clogged or damaged. In many cases, replacing the carburetor is quicker and only slightly more costly.
Function: Mixes air and fuel in the proper ratio to create a combustible mixture that powers the engine. This mixture is then delivered to the combustion chamber where it ignites and drives the piston.
How to Fix When Faulty: If the engine starts momentarily with starter fluid but stalls shortly after, the carburetor is likely clogged or damaged. In many cases, replacing the carburetor is quicker and only slightly more costly.

Replacing the carburetor helps you save cost (Source: AZParts)
1.3. Air Filter / Air Cleaner
Location: The air filter is positioned at the front of the mower and is connected directly to the carburetor.
Function: Its primary role is to clean incoming air by trapping dust and debris before the air reaches the combustion chamber. This helps protect the engine from damage and ensures optimal performance.
How to Fix When Faulty: If the air filter becomes clogged or damaged, it restricts airflow to the carburetor, which can affect fuel mixture and engine efficiency. To fix this, clean lawn mower air filter if it is reusable or replace the air filter if it is too dirty or worn out.
1.4. Recoil Starter
Location: Attached to the engine housing, the recoil starter consists of a rope mechanism designed to spin the engine’s crankshaft.
Function: When you pull the recoil starter rope, it rotates the crankshaft, initiating the engine’s ignition process. This component is vital for starting the grass cutter machine.
How to Fix When Malfunctioning:
- If the recoil starter rope is stuck, remove the starter assembly, check for jammed parts, and rewind the rope properly.
- If the rope or spring is damaged, replace them with new parts and reinstall the assembly.

Recoil Starter from AZParts is high-quality (Source: AZParts)
1.5. Ignition System (Ignition Coil and Spark Plug)
Location: The ignition coil is typically positioned next to the flywheel on the engine.
Function: The ignition coil’s role is to generate a high-voltage electric current when the flywheel magnets rotate past it. This current is then delivered to the spark plug, which produces a spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture inside the engine cylinder. Without a functioning ignition coil, the spark plug will not fire, preventing the engine from starting.
How to Fix When Faulty: If the ignition coil fails to send electric current to the spark plug, the engine will not start. If the ignition coil is confirmed faulty, replace it to ensure the ignition coil properly sends current to the spark plug, restoring engine ignition.
1.6. Flywheel
Location: Attached to the rear end of the crankshaft inside the engine housing.
Function: The flywheel stores rotational energy to maintain engine momentum and smooth out power delivery during operation. It also helps in starting the engine by engaging with the starter motor.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: The flywheel stores rotational energy to maintain engine momentum and smooth out power delivery during operation. It also helps in starting the engine by engaging with the starter motor.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Inspect for cracks, wear, or imbalance.
- Replace if damaged or warped.
- Ensure proper mounting and torque on flywheel bolts to prevent loosening.
1.7. Crankcase Engine
Location: The main body of the engine housing, enclosing the crankshaft and related components.
Function: Provides structural support and protection for internal moving parts, and contains the lubricating oil to ensure smooth operation.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: Provides structural support and protection for internal moving parts, and contains the lubricating oil to ensure smooth operation.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Check for oil leaks or cracks in the casing.
- Replace gasket or seals if leaking.
- Repair or replace the crankcase if cracked or severely damaged to avoid oil loss or contamination.

Fix Crankcase Engine Issues by Replacing Gasket (Source: AZParts)
1.8. Piston and Piston Ring
Location: Inside the cylinder bore of the engine block.
Function: The piston converts combustion pressure into mechanical force; the piston rings provide a seal between the piston and cylinder wall to maintain compression and control oil consumption.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: The piston converts combustion pressure into mechanical force; the piston rings provide a seal between the piston and cylinder wall to maintain compression and control oil consumption.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Inspect piston and rings for wear, scoring, or damage.
- Replace worn or broken piston rings to restore compression.
- If the piston is damaged, replace it and re-check cylinder bore for wear or scoring.
1.9. Crankshaft and Connecting Rod
Location: Inside the crankcase, connected between the piston and the flywheel.
Function: The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the piston into rotational motion; the connecting rod transmits force from the piston to the crankshaft.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the piston into rotational motion; the connecting rod transmits force from the piston to the crankshaft.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Check for signs of wear, cracks, or bending.
- Replace bearings or bushings as necessary.
- Replace or recondition the crankshaft and connecting rod if damaged to prevent engine failure.
1.10. Oil Seal

Oil Seal in Lawn Mower (Source: AZParts)
Location: Positioned at various points where the rotating parts exit the engine casing, such as around the crankshaft or camshaft.
Function: Prevents oil leakage from the engine while allowing shafts to rotate freely.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: Prevents oil leakage from the engine while allowing shafts to rotate freely.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Replace the oil seal if leaking or hardened.
- Clean the sealing surface before installation.
- Ensure proper alignment and fit to avoid premature failure.
2. Transmission and Drive System of Lawn Mower

Transmission and Drive System of Lawn Mower (Source: AZParts)
2.1. Clutch
Location: Positioned between the engine and the transmission, usually mounted near the engine output shaft or integrated into the pulley system.
Function: The clutch engages or disengages the power flow from the engine to the transmission, allowing the lawn mower to stop or start moving without shutting down the engine. It also facilitates smooth gear shifting during operation.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: The clutch engages or disengages the power flow from the engine to the transmission, allowing the lawn mower to stop or start moving without shutting down the engine. It also facilitates smooth gear shifting during operation.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Check for slipping, unusual noises, or failure to engage/disengage.
- Inspect clutch plates, springs, and linkages for wear or misalignment.
- Replace worn-out clutch components such as friction plates or springs.
- Adjust cable tension or hydraulic pressure (if applicable) to restore correct function.
- Clean any debris or oil that may be causing clutch slippage.
2.2. Clutch Housing

Clutch Housing Lawn Mower (Source: AZParts)
Location: Encases the clutch assembly, typically attached to the engine block or transmission casing.
Function: Protects the clutch components from dirt, debris, and moisture. It also helps in aligning the clutch parts correctly and may assist in heat dissipation during operation.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: Protects the clutch components from dirt, debris, and moisture. It also helps in aligning the clutch parts correctly and may assist in heat dissipation during operation.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Inspect for cracks, deformations, or loose mounting bolts.
- Clean out any buildup of grass, debris, or oil that may interfere with operation.
- Replace damaged or warped housing to ensure proper clutch alignment.
- Check the integrity of sealing surfaces to prevent contamination of internal parts.
2.3. Flexible Shaft
Location: Runs from the clutch or engine area to the transmission or wheel hub, depending on the drive design. Often enclosed in a protective casing and routed through the chassis of the mower.
Function: Transmits rotary motion from the engine to other components like the wheels or cutting blades while allowing for flexibility in routing through the mower’s frame. Ideal for compact or curved designs.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: Transmits rotary motion from the engine to other components like the wheels or cutting blades while allowing for flexibility in routing through the mower’s frame. Ideal for compact or curved designs.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Check for excessive vibration, lack of power transmission, or unusual noise.
- Inspect the shaft for fraying, kinks, or breakage inside the casing.
- Lubricate the shaft if required (some are sealed and non-serviceable).
- Replace the shaft if damaged or if internal wire strands are worn or snapped.
- Ensure proper alignment and secure attachment at both ends to prevent excessive wear.
3. Cutting Mechanism on Lawn Mower

Cutting Mechanism on Lawn Mower (Source: AZParts)
3.1. Blade Housing
Location: Mounted underneath the lawn mower deck, surrounding and shielding the cutting blade(s). Often forms part of the mower’s lower chassis.
Function: The blade housing (also called the mower deck) serves as a protective enclosure for the rotating blade. It directs grass clippings into the discharge chute or collection bag, and also ensures operator safety by containing debris and blade fragments.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: The blade housing (also called the mower deck) serves as a protective enclosure for the rotating blade. It directs grass clippings into the discharge chute or collection bag, and also ensures operator safety by containing debris and blade fragments.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Inspect for rust, dents, or cracks, especially around mounting points.
- Clean out accumulated grass clippings and debris regularly to prevent clogging.
- Repair minor rust or dents using patch kits; replace if severely corroded or deformed.
- Check that the housing is securely mounted and that safety shields are intact.
- Ensure blade clearance is not obstructed by a warped or damaged deck.
3.2. Grass-cutting Blade
Location: Attached directly to the blade shaft or motor spindle, located within the blade housing at the underside of the lawn mower.
Function: The blade rotates at high speed to cut grass evenly. It may be designed for mulching, side discharge, or bagging, depending on the mower model.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: The blade rotates at high speed to cut grass evenly. It may be designed for mulching, side discharge, or bagging, depending on the mower model.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Sharpen the blade regularly for clean and efficient cutting.
- Inspect for bending, cracks, or excessive wear replace if damaged.
- Balance the blade during sharpening to prevent vibration and uneven cutting.
- Ensure blade bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Use only blades designed for your mower model to maintain cutting performance and safety.
4. Control and Support Mower Components

Control and Support Parts on Lawn Mower (Source: AZParts)
4.1. Brake Lever
Location: Typically mounted on the upper handlebar, easily accessible to the operator’s hand.
Function: The brake lever is used to engage or disengage the braking mechanism, stopping the blade or wheels when released. It enhances operator safety by ensuring that the blade or drive system halts when the lever is not held.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: The brake lever is used to engage or disengage the braking mechanism, stopping the blade or wheels when released. It enhances operator safety by ensuring that the blade or drive system halts when the lever is not held.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Check for stiffness, looseness, or failure to engage the brake.
- Inspect the cable for fraying, stretching, or detachment replacement if damaged.
- Lubricate pivot points to improve movement.
- Adjust cable tension to ensure effective braking.
- Replace the brake lever assembly if broken or non-responsive.
4.2. Cutting Height Adjustment Lever

Cutting Height Adjustment Lever on Lawn Mower (Source: AZParts)
Location: Located near the wheels or on the mower deck, often one lever per wheel or a centralized lever depending on the model.
Function: Allows the user to raise or lower the cutting height of the blade by adjusting the position of the wheels or deck. This lets the mower adapt to different grass lengths or user preferences.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: Allows the user to raise or lower the cutting height of the blade by adjusting the position of the wheels or deck. This lets the mower adapt to different grass lengths or user preferences.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Check for stiffness, rust, or inability to lock into height positions.
- Clean and lubricate moving joints or locking teeth.
- Replace the lever or height adjustment mechanism if bent or damaged.
- Ensure the wheels are properly aligned after adjustment for even cutting.
4.3. Grass Bag
Location: Attached at the rear or side of the mower, depending on discharge direction.
Function: Collects grass clippings during operation, keeping the lawn tidy and reducing the need for raking.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: Collects grass clippings during operation, keeping the lawn tidy and reducing the need for raking.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Inspect for tears, holes, or loose stitching.
- Clean out debris or wet clippings to avoid blockages and bad odors.
- Replace the bag if the mesh is damaged or unable to hold clippings.
- Ensure it is properly secured to the mower frame to prevent clippings from escaping.
4.4. Wheels

Wheels in Lawn Mower (Source: AZParts)
Location: Mounted on the mower’s base, typically four wheels attached near each corner of the chassis.
Function: Support the mower and allow it to roll smoothly across various lawn surfaces. Wheel height often correlates with cutting height settings.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: Support the mower and allow it to roll smoothly across various lawn surfaces. Wheel height often correlates with cutting height settings.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Inspect for wobbling, cracks, or uneven wear.
- Replace damaged or worn-out wheels.
- Tighten or replace axles or fasteners if wheels become loose.
- Lubricate wheel bearings or bushings if movement feels restricted.
4.5. Handle
Location: Extends upward and backward from the mower base, used for pushing and steering.
Function: Provides the operator with control over mower movement and access to operational controls like the brake lever or throttle. Often foldable for storage.
How to Fix When Faulty:
Function: Provides the operator with control over mower movement and access to operational controls like the brake lever or throttle. Often foldable for storage.
How to Fix When Faulty:
- Tighten any loose bolts or locking knobs.
- Replace if bent, cracked, or unstable during use.
- Check for comfortable grip and control add handle padding or replace grips if worn.
- Ensure folding or height-adjustment mechanisms work smoothly and lock securely.
5. FAQs about Lawn Mower Parts Name
5.1. What is included in a lawn mower tune up?
A lawn mower tune-up typically includes changing the engine oil, replacing the air filter and spark plug, sharpening or replacing the cutting blade, checking and adjusting the drive belt, cleaning the deck and fuel system, and inspecting the overall condition of cables, wheels, and safety features.
5.2. What are spindles on a lawn mower?
Spindles are mechanical components that connect the mower blades to the deck and allow them to rotate. They typically consist of a shaft and bearing assembly that transfers power from the belt or engine to the cutting blades. Worn or damaged spindles can cause uneven cutting or blade vibration.
5.3. How many years should a lawn mower last?
With proper maintenance, a quality lawn mower can last anywhere from 8 to 15 years or more. The lifespan depends on usage frequency, mower type (gas, electric, or manual), and whether regular servicing and part replacements are carried out.
5.4. What is the main item to be replaced during a tune-up?
The spark plug is usually the main item replaced during a tune-up, as it’s crucial for engine ignition. Additionally, the air filter and engine oil are commonly changed to ensure efficient engine performance and longevity.
Lawn mower maintenance with proper care and timely part replacements is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the names, locations, and functions of each component helps you identify lawn mower troubleshooting early and carry out effective repairs. If you're looking for high-quality replacement parts, AZParts offers a wide selection of lawn mower parts compatible with many popular brands. Whether you need blades, lawn mower kit, filters, cables, or drive parts, AZParts provides reliable solutions to keep your equipment running smoothly season after season.
Contact Information:
8 The Green, Ste A, Dover, Delaware 19901-3618, United States
Read more:
Lawn Mower
Further Reading
Further Reading





